Syphilis
What is syphilis?
Syphilis is an STD that has been around for centuries.
It is caused by a microscopic bacterial organism called a spirochete. The
scientific name for the organism is Treponema pallidum. The spirochete is a
wormlike, spiral-shaped organism that wiggles vigorously when viewed under a
microscope. It infects the person by burrowing into the moist, mucous-covered
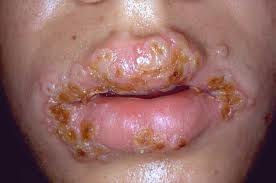
lining of the mouth or genitals. The spirochete produces a classic, painless
ulcer known as a chancre.
Symptoms of syphilis
There are three stages of syphilis, along with an
inactive (latent) stage. Formation of an ulcer (chancre) is the first stage.
The chancre develops any time from 10 to 90 days after infection, with an
average time of 21 days following infection until the first symptoms develop.
Syphilis is highly contagious when the ulcer is present.
The infection can be transmitted from contact with the
ulcer which teems with spirochetes. If the ulcer is outside of the vagina or on
the male's scrotum, condoms may not prevent transmission of the infection by
contact. Similarly, if the ulcer is in the mouth, merely kissing the infected
individual can spread the infection. The ulcer can resolve without treatment
after three to six weeks, but the disease can recur months later as secondary
syphilis if the primary stage is not treated.
 In most women, an early infection resolves on its own,
even without treatment. However, 25% will proceed to the second stage of the
infection called "secondary" syphilis, which develops weeks to months
after the primary stage and lasts from four to six weeks. Secondary syphilis is
a systemic stage of the disease, meaning that it can involve various organ
systems of the body. In this stage, patients can initially experience many
different symptoms, but most commonly they develop a skin rash, typically
appearing on the palms of the hands or the bottoms of the feet, that does not
itch. Sometimes the skin rash of secondary syphilis is very faint and hard to
recognize; it may not even be noticed in all cases. This secondary stage can
also include hair loss, sore throat, white patches in the nose, mouth, and
vagina, fever, and headaches. There can be lesions on the genitals that look
like genital warts but are caused by spirochetes rather than the wart virus.
These wartlike lesions, as well as the skin rash, are highly contagious. The
rash can occur on the palms of the hands, and the infection can be transmitted
by casual contact.
In most women, an early infection resolves on its own,
even without treatment. However, 25% will proceed to the second stage of the
infection called "secondary" syphilis, which develops weeks to months
after the primary stage and lasts from four to six weeks. Secondary syphilis is
a systemic stage of the disease, meaning that it can involve various organ
systems of the body. In this stage, patients can initially experience many
different symptoms, but most commonly they develop a skin rash, typically
appearing on the palms of the hands or the bottoms of the feet, that does not
itch. Sometimes the skin rash of secondary syphilis is very faint and hard to
recognize; it may not even be noticed in all cases. This secondary stage can
also include hair loss, sore throat, white patches in the nose, mouth, and
vagina, fever, and headaches. There can be lesions on the genitals that look
like genital warts but are caused by spirochetes rather than the wart virus.
These wartlike lesions, as well as the skin rash, are highly contagious. The
rash can occur on the palms of the hands, and the infection can be transmitted
by casual contact.
Subsequent to secondary syphilis, some patients will
continue to carry the infection in their body without symptoms. This is the
so-called latent stage of the infection. Then, with or without a latent stage,
which can last as long as 20 or more years, the third (tertiary) stage of the
disease can develop. At this stage, syphilis usually is no longer contagious.
Tertiary syphilis is also a systemic stage of the disease and can cause a
variety of problems throughout the body including:
abnormal bulging of the large vessel leaving the heart
(the aorta), resulting in heart problems;
the development of large nodules (gummas) in various
organs of the body;
infection of the brain, causing a stroke, mental
confusion, meningitis (type of brain infection), problems with sensation, or
weakness (neurosyphilis);
involvement of the eyes leading to sight deterioration;
or
involvement of the ears resulting in deafness. The
damage sustained by the body during the tertiary stage of syphilis is severe
and can even be fatal.
Diagnosis of syphilis
Syphilis can be diagnosed by scraping the base of the
ulcer and looking under a special type of microscope (dark field microscope)
for the spirochetes. However, since these microscopes are rarely detected, the
diagnosis is most often made and treatment is prescribed based upon the
appearance of the chancre. Diagnosis of syphilis is complicated by the fact
that the causative organism cannot be grown in the laboratory. Therefore,
cultures of affected areas cannot be used for diagnosis.
Special blood tests can also be used to diagnose
syphilis. The standard screening blood tests for syphilis are called the
Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) and Rapid Plasminogen Reagent (RPR)
tests. These tests detect the body's response to the infection, but not to the
actual Treponema organism that causes the infection. These tests are thus
referred to as non-treponemal tests. Although the non-treponemal tests are very
effective in detecting evidence of infection, they can also produce a positive
result when no infection is actually present (so-called false-positive results
for syphilis). Consequently, any positive non-treponemal test must be confirmed
by a treponemal test specific for the organism causing syphilis, such as the
microhemagglutination assay for T. pallidum (MHA-TP) and the fluorescent
treponemal antibody absorbed test (FTA-ABS). These treponemal tests directly
detect the body's response to Treponema pallidum.
Treatment of syphilis
Depending on the stage of disease and the clinical
manifestations, the treatment options for syphilis vary. Long-acting penicillin
injections have been very effective in treating both early and late stage
syphilis. The treatment of neurosyphilis requires the intravenous
administration of penicillin. Alternative treatments include oral doxycycline
or tetracycline.
Women who are infected during pregnancy can pass on the
infection to the fetus through the placenta. Penicillin must be used in
pregnant patients with syphilis since other antibiotics do not effectively
cross the placenta to treat the infected fetus. Left untreated, syphilis can
lead to blindness or even death of the infant.