THE INTRA-UTERINE DEVICE [I.U.D]
Intrauterine devices – they are contraceptives which are used all over the world they are devices which are inserted to the uterus they halt conception in different ways some help in the prevention of fertilization to take place while others disrupt normal ovulation patterns.
Types of intra uterine devices
First generation of I.U.D
1. LIPPES LOOP
It is a double – S. shaped device made up of polythene, which is non toxic non tissue reactive and extremely durable. it contains small amount of barium sulfate to allow x-ray observation .the loop has attached thread made of fine nylon lippes is available in different sizes iit is a an old method of I.U.D which is not used nowadays
SECOND GENERATION
2. COPPER .T
It was found out that metallic copper had a strong anti fertility effect. Copper I.U.D is available in many
varieties they are more effective and can be left for a long time used by women worldwide
ADVANTAGES OF COPPER DEVICES
· low expulsion rate
· low incidence of side effects e.g pain
· increased contraceptives effectiveness
· Effective as post-coital contraceptives ,if inserted within 2-4days of unprotected sex
THIRD GENERATIONS
This group of I.U.D is based on the principles of release of hormones
A. HORMONAL REALESE PROGESTASERT-T SHAPE(paragard)
In progestasert there is natural hormone progesterone and its release slowly in the uterus at rate of 65mcg daily
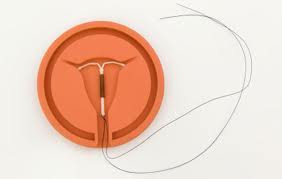
Mirena® contains a small amount of progesterone, a natural ovarian hormone, that keeps the inside lining of your uterus thin. This results in lighter periods and less menstrual cramps that many women desire. It works so well that we often use the Mirena® IUD to help women who experience abnormally heavy periods.
Which continuously releases a small amount of the progestin levonorgestreland is effective for 5 years
The Mirena intrauterine device (IUD) is a small, "T-shaped" contraceptive device made of flexible plastic and must be inserted by a qualified health-care professional (such as an ob/gyn or nurse practitioner). Mirena releases a low amount of progestin levonorgestrel continuously over a 5-year period as a way to prevent pregnancy
The Mirena IUD has strings attached that hang down through the cervix into the vagina. Depending on how short the strings are cut, a woman can make sure the IUD is in place by feeling for the strings. A doctor uses the strings to remove the IUD. Some woman may have the strings cut shorter if they are felt by the woman’s sexual partner.
When this is the case, sometimes the strings are cut so short that the woman cannot actually check for the strings. If this does not apply to you, it is wise to feel for the string end between periods.
It is especially important to check every few days for the first few months to make sure that it is still properly in place. That being said, one of the greatest advantages of the Mirena IUD is that, for the most part, once it has been inserted everything is perfect .levenorgestrel is a synthetics steroids releasing 20mcg of levenorgestrel.
Advantages
Difference between an IUD and an IUS
An intrauterine system (IUS) is a small plastic device that is inserted into the uterus and slowly releases a hormone called progestogen. An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small plastic and copper device that does not contain any hormone.
Effectiveness of an IUD
When this is the case, sometimes the strings are cut so short that the woman cannot actually check for the strings. If this does not apply to you, it is wise to feel for the string end between periods.
It is especially important to check every few days for the first few months to make sure that it is still properly in place. That being said, one of the greatest advantages of the Mirena IUD is that, for the most part, once it has been inserted everything is perfect .levenorgestrel is a synthetics steroids releasing 20mcg of levenorgestrel.
Advantages
· It
works as soon as it is put in.
·
It
works for 5–10 years depending on type (but can be taken out sooner).
·
It
doesn’t interrupt sex.
·
It
can be used if you are breastfeeding.
·
Your
fertility returns to normal as soon as the IUD is taken out.
·
It
is not affected by other medicines.
Disadvantages
- Your
periods may be heavier, longer or more painful.
- This may improve after a few
months
- You
will first need an internal examination to check the IUD is suitable, and
another when it is fitted.
- The
IUD does not protect you from sexually transmitted infections, so you may have
to use condoms as well. If you get an infection when an IUD is in place this
could lead to a pelvic infection if it is not treated.
COMPLICATIONS AND RISKS OF IUD
·
There
is a very small chance of you getting an infection during the first 20 days
after an IUD is put in. You may be advised to have a check for any possible
existing infection before an IUD is fitted.
·
The
IUD can be pushed out by your uterus (expulsion) or it can move (displacement).This
is not common. This is more likely to happen soon after it has been put in and
you may not know it has happened. This is why your doctor or nurse will teach
you how to check your IUD threads every month.
·
It
is not common, but there is a risk that an IUD might go through (perforate)
your uterus or cervix when it is put in. This may cause pain but often there
are no symptoms. If it happens, the IUD may have to be removed by surgery. The
risk of perforation is low when an IUD is fitted by an experienced doctor or
nurse.
·
If
you do become pregnant while you are using an IUD there is a small increased
risk of you having an ectopic pregnancy).The risk of ectopic pregnancy is less
in women using an IUD than in women using no contraception at all.
Difference between an IUD and an IUS
An intrauterine system (IUS) is a small plastic device that is inserted into the uterus and slowly releases a hormone called progestogen. An intrauterine device (IUD) is a small plastic and copper device that does not contain any hormone.
Effectiveness of an IUD
Depends
on how old you are, how often you have sex and whether you follow the
instructions given by a qualified health professionalThere
are different types of IUDs. Newer IUDs contain more copper and are the most
effective – over 99 per cent effective. This means less than two women in 100
will get pregnant over five years. Older IUDs have less copper and are less
effective.
The
IUD is a long-acting reversible method of contraception. All long-acting methods are effective
because while they are being used you do not have to remember to take or use
contraception.